#478
Introduction:
Voting stands as the cornerstone of democratic societies, embodying the power of the individual voice to shape the collective future. It's a fundamental right and a civic duty that empowers citizens to participate actively in the governance of their nations. With each vote cast, we affirm our commitment to shaping policies, electing representatives, and steering the course of our communities and countries.
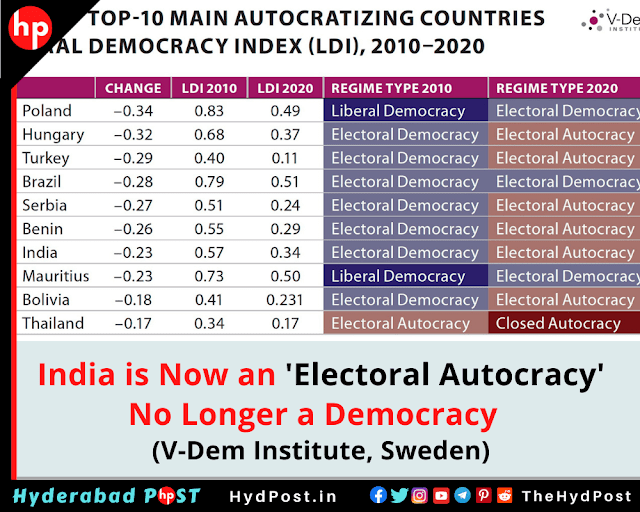
Yet, amidst the significance of voting lies a growing challenge: the rise of electoral autocracy in nations like here in India, Russia, and Turkey. Despite their democratic façades, these countries grapple with the erosion of democratic norms, the centralization of power, and the suppression of dissenting voices. In India, the world's largest democracy, concerns linger about the health of democratic institutions, while Russia and Turkey witness the consolidation of power in the hands of ruling elites.
As Indian elections loom on the horizon, scheduled to commence next week, on April 26th, I find myself eagerly anticipating the opportunity to exercise my franchise once again here in Bangalore. Having participated in the electoral process for over 15 years, I recognize the significance of each vote and the role it plays in shaping the destiny of our nation. Despite the challenges posed by electoral autocracy, I remain committed to upholding the principles of democracy and contributing to a future founded on transparency, accountability, and the will of the people. Also America goes to Polls on November 5th, a historic verdict expected one way or the other.
+++++
Why Voting Matters:
Voice in Democracy:Voting is the essence of democracy, providing individuals with a direct channel to voice their opinions, concerns, and aspirations.Accountability:
It ensures that every citizen, regardless of background or status, has an equal opportunity to influence the direction of their society.
Through voting, citizens hold elected officials accountable for their actions and decisions.Representation:
It serves as a mechanism to ensure that those in power remain responsive to the needs and interests of the people they represent.
Voting contributes to the diversity of voices and perspectives in government.Impact on Policies:
It ensures that policies reflect the multifaceted needs and values of society, fostering inclusivity and representation for all segments of the population.
Each vote casts a ripple effect on the formulation and implementation of policies.Community Engagement:
It influences decisions on crucial issues such as healthcare, education, the environment, and social welfare, shaping the quality of life for individuals and communities.
Voting fosters civic engagement and community involvement, encouraging people to stay informed about current affairs and participate in public discourse.Global Impact:
It strengthens the social fabric by promoting dialogue, collaboration, and collective action towards shared goals.
In an interconnected world, the outcomes of elections have far-reaching implications beyond national borders.
Voting influences international relations, trade agreements, climate policies, and human rights agendas, shaping the global landscape for generations to come.
In essence, voting matters because it empowers individuals to shape their societies, hold their leaders accountable, and contribute to a more inclusive, responsive, and equitable world.
+++++
Election Cynicism:
Growing Apathy on Electoral Process:
- Across the globe, there's a rising sense of apathy towards the electoral process, with many individuals feeling disillusioned and disconnected from politics.
- Factors such as political scandals, lack of trust in institutions, and perceived inefficacy of voting contribute to this cynicism.
Low Voter Turnout in Big Cities:
- In most developed countries, including India, voter turnout in big cities tends to be significantly lower compared to rural areas.
- Urban populations often face barriers such as long lines, voter registration issues, and competing priorities, leading to decreased participation.
Influence of Freebies and Promises:
- Political parties often resort to offering freebies, cash, or concessions to entice voters, especially in developing countries.
- While these incentives may temporarily sway voters, they raise concerns about the integrity of the electoral process and the motives of elected officials.
Electoral Politics as Business:
- There's a pervasive perception that electoral politics is no longer about serving the people or the nation but rather about maximizing returns on investment.
- The influence of money in politics, corporate interests, and lobbying undermine the democratic principles of representation and accountability.
Despite these challenges, it's essential to recognize the importance of civic engagement and the potential for change through collective action. Addressing issues such as voter education, campaign finance reform, and transparency in governance can help restore trust in the electoral process and revitalize democracy.
+++++
Electoral Autocracy: Challenges in India, Russia, and Turkey:
India:
- Erosion of Democratic Norms:
- Increasing instances of erosion in democratic norms, including attacks on freedom of speech and press, and weakening of institutional checks and balances.
- Centralization of Power:
- The concentration of power in the hands of the ruling party, diminishing the autonomy of democratic institutions and hindering the effectiveness of democratic governance.
- Restrictions on Freedom:
- Imposition of restrictions on freedom of expression, assembly, and association, limiting the ability of citizens to participate fully in the democratic process.
- Divisive Politics:
- Politicization of identity-based issues leading to societal divisions, polarization, and erosion of social cohesion, undermining the pluralistic fabric of Indian democracy.
Russia:
- Consolidation of Power under Putin:
- Persistent consolidation of power in the hands of Vladimir Putin and his ruling party, stifling political pluralism and fostering a climate of political dominance.
- Lack of Competition and Transparency:
- Absence of genuine political competition and transparency in electoral processes, with opposition voices marginalized and independent media suppressed.
- Suppression of Opposition:
- Systematic suppression of political opposition through intimidation, harassment, and imprisonment, limiting the space for dissent and political pluralism.
- Kremlin's Influence:
- The pervasive influence of the Kremlin in shaping electoral outcomes and political narratives, undermining the credibility and integrity of Russia's electoral system.
Turkey:
- Authoritarian Drift under Erdoğan:
- The gradual drift towards authoritarianism under Recep Tayyip Erdoğan's leadership, characterized by the erosion of democratic institutions and the consolidation of executive power.
- Crackdowns on Dissent:
- Widespread crackdowns on political dissent, civil society, and media freedom, restricting the space for political opposition and civil liberties.
- Executive Power Concentration:
- Increasing concentration of executive power in the presidency, weakening the system of checks and balances and diminishing parliamentary oversight.
- Electoral Polarization:
- Heightened electoral polarization fueled by divisive rhetoric, polarization, and the marginalization of minority voices, exacerbating social tensions and undermining democratic consensus-building.
These challenges underscore the urgent need for safeguarding democratic principles, promoting transparency, accountability, and respect for human rights, and fostering inclusive and participatory political systems in India, Russia, Turkey, and beyond.
Conclusion:
As we navigate the complexities of electoral autocracy in countries like India, Russia, and Turkey, it becomes increasingly evident that the importance of voting cannot be overstated. Despite the challenges posed by erosion of democratic norms, centralization of power, and suppression of dissent, the act of voting remains a powerful tool in the hands of citizens to shape the course of their nations. In the face of electoral autocracy, it is imperative that we defend democratic institutions and uphold the principles of transparency and accountability in electoral processes. By holding elected officials accountable for their actions and demanding integrity in governance, we can work towards safeguarding the integrity of our democratic systems.
Furthermore, we must recognize the significance of safeguarding fundamental rights and freedoms amidst authoritarian trends. Protecting freedom of speech, press, and assembly is essential for fostering a vibrant and inclusive democratic society where all voices are heard and respected.
In conclusion, let us embrace the responsibility that comes with the privilege of voting, and let us stand united in our commitment to defending democracy, promoting transparency, and safeguarding the rights and freedoms of all individuals, both within our own countries and across the globe. Together, we can strive towards a future founded on the principles of justice, equality, and democratic governance.
Karthik
14/4/24 Tamil New Years day.
11am.